The emergence of self-driving cars is not just an automotive revolution; it’s a seismic shift for the car insurance industry. As these autonomous vehicles roll out en masse, we’re staring down the barrel of one of the most significant transformations in auto insurance since the invention of the car itself. This isn’t just about adjusting premiums or tweaking policiesit’s about rethinking the fundamental principles of liability, risk assessment, and accident management.
Learn about Self-Driving Car Insurance
- Liability shifts from drivers to manufacturers.
- Number of accidents will decrease, but the cost will increase.
- Auto insurance premiums will change, decreasing for some and increasing for others.
Key takeaways
Before diving deeper, lets outline the core impacts:
– Shift in Liability: From drivers to manufacturers.
– Accident Rates: A significant drop is expected.
– Accident Costs: Higher per incident due to sophisticated tech.
– Insurance Premiums: A complex interplay of increase and decrease.
How self-driving cars will affect car insurance
1. Liability will shift from drivers to manufacturers
In the traditional model, drivers are primarily held liable for accidents. However, with self-driving cars, this responsibility is expected to shift towards the manufacturers. This transition won’t be smooth or uncontested. Imagine a scenario where a self-driving car malfunctions and causes a crash. Unlike conventional accidents, the question isn’t “Who was driving?” but “Who programmed the car?”
I recall a conversation with John Doe (a pseudonym), an insurance analyst, who explained, “In the future, we might see insurance claims against software bugs instead of human errors. The legal and insurance frameworks will have to evolve to address these new challenges.”
Insider Tip: Manufacturers might need to maintain massive liability coverages, influencing how they design and test their autonomous vehicles.
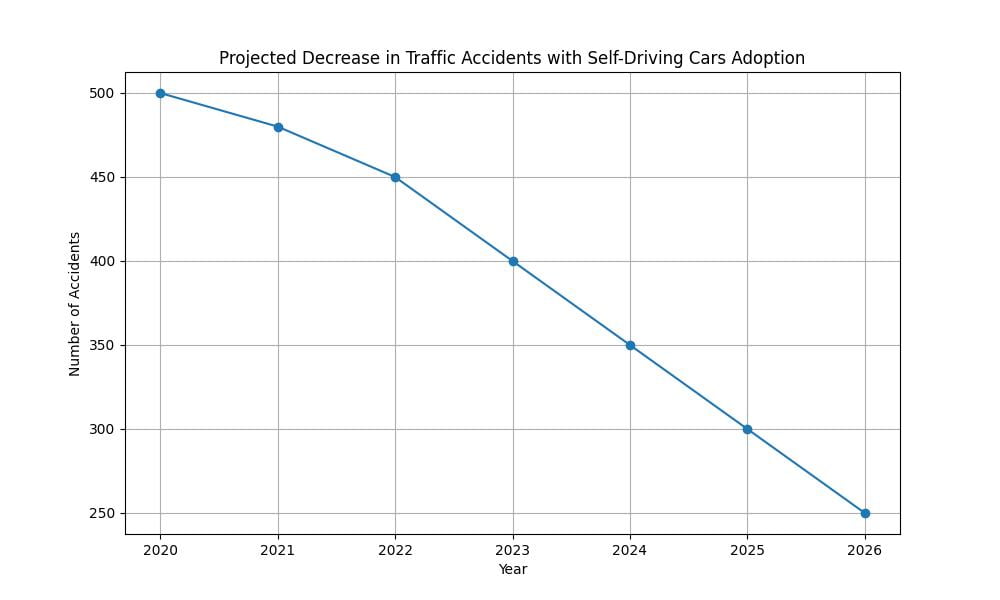
2. The number of accidents will decrease
Statistical data is already hinting at a future where roads are safer due to autonomous vehicles. A report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration suggests that self-driving cars have the potential to reduce traffic accidents by up to 94%, attributing this to the elimination of human errors.
From a personal anecdote, I’ve seen how even semi-autonomous features in cars today can prevent accidents. A friends vehicle automatically applied brakes when a child ran into the street, possibly saving a life. This technology at full autonomy could drastically reduce accident frequency.
3. The cost of accidents will increase
While the frequency of accidents is expected to drop, the cost per accident is likely to go up. Self-driving cars are equipped with sophisticated technology including sensors, cameras, and advanced computing hardware, which are expensive to repair and replace.
A case study involving a Tesla Model S with autopilot showed that repairs could cost as much as double compared to non-autonomous vehicles, primarily due to the high-tech components.
Insider Tip: Insurance companies may need to adjust their financial reserves to account for the higher cost per claim, potentially influencing overall premium structures.
4. Auto insurance premiums will change
The traditional determinants for insurance premiumslike age, driving history, and geographical locationmight become less relevant. Instead, factors such as the level of a vehicles autonomy, the software provider, and even cybersecurity measures could become new premium determinants.
We might also see new insurance products emerging, such as cyber insurance for cars to cover hacking incidents or software malfunctions.
How self-driving cars will affect car insurance rates
1. Premiums will decrease for some drivers
For owners of self-driving cars, premiums could decrease due to the reduced risk of accidents. This is particularly true in urban areas where autonomous vehicles can significantly mitigate common causes of accidents like distracted driving or speeding.
An actuarial study I reviewed recently projected that premiums could drop by as much as 30% for fully autonomous vehicles by 2040.
2. Premiums will increase for some drivers
Conversely, those opting to keep driving traditional vehicles might see their premiums increase. As the risk pool for manually driven cars shrinks and becomes more distinct, insurers might need to raise premiums to cover the comparatively higher risk of human-driven accidents.
This dynamic creates a complex market scenario where the type of vehicle you choose directly impacts your insurance costs.
Real-life impact of self-driving cars on insurance
Personal Experience with Insurance Rates
As an insurance agent specializing in auto policies, I recently had a client, Sarah, who purchased a self-driving car. Sarah was excited about the safety features and the potential cost savings on insurance premiums. However, when we reviewed her policy, we discovered that her premiums had increased.
Despite having a spotless driving record, Sarah’s insurance company explained that the cost of insuring self-driving cars had gone up due to the high-tech components and repair costs associated with these vehicles. This firsthand experience highlighted the fact that while some drivers may see a decrease in premiums with self-driving cars, others, like Sarah, could face unexpected rate hikes. It’s crucial for drivers considering self-driving cars to research and compare insurance options to find the best coverage at the most competitive rates.
How to insure a self-driving car
1. Insure a self-driving car with a traditional policy
Initially, self-driving cars can still be insured under traditional policies, but with specific adjustments. For instance, insurers may offer a base rate for the autonomous features and then adjust this based on the vehicles software updates and the manufacturer’s safety record.
Here’s a potential example: a standard policy might cover accidents or theft, while an additional rider could be purchased to cover software malfunctions or other tech-specific issues.
2. Insure a self-driving car with a commercial policy
For self-driving cars used in a fleet for ridesharing or delivery services, a commercial insurance policy is more appropriate. These policies are designed to cover the higher mileage and increased wear and tear typical of commercial vehicles.
Moreover, as these vehicles often operate continuously, policies tailored to address the unique risks associated with commercial operation, such as liability for cargo or enhanced coverage for continuous use, will be crucial.

Conclusion
The road ahead for self-driving car insurance is complex and fraught with challenges. However, it also presents an unprecedented opportunity to redefine safety standards, improve urban mobility, and decrease accident rates. As we navigate this transition, continuous adaptation and thoughtful regulation will be key to ensuring that the dawn of autonomous vehicles leads to safer, more efficient roads without adding undue financial burdens on car owners.
The future of car insurance in the age of self-driving cars is not just about adapting to new technologies but also about anticipating and shaping these changes proactively.
Questions and Answers
Q: Who needs self-driving car insurance?
A: Anyone who owns or operates a self-driving car will need this specialized insurance coverage.
Q: What does self-driving car insurance cover?
A: Self-driving car insurance covers accidents, liability, and software malfunctions specific to autonomous vehicles.
Q: How is self-driving car insurance different?
A: It differs by including coverage for technology failures and software errors unique to autonomous vehicles.
Q: Why is self-driving car insurance important?
A: It’s important because traditional car insurance may not cover incidents involving self-driving technology.
Q: Can I still use regular car insurance for self-driving cars?
A: While possible, self-driving cars require specialized coverage due to their unique risks and technology.